Operation Hold the Line 1993

Operation Hold the Line 1993
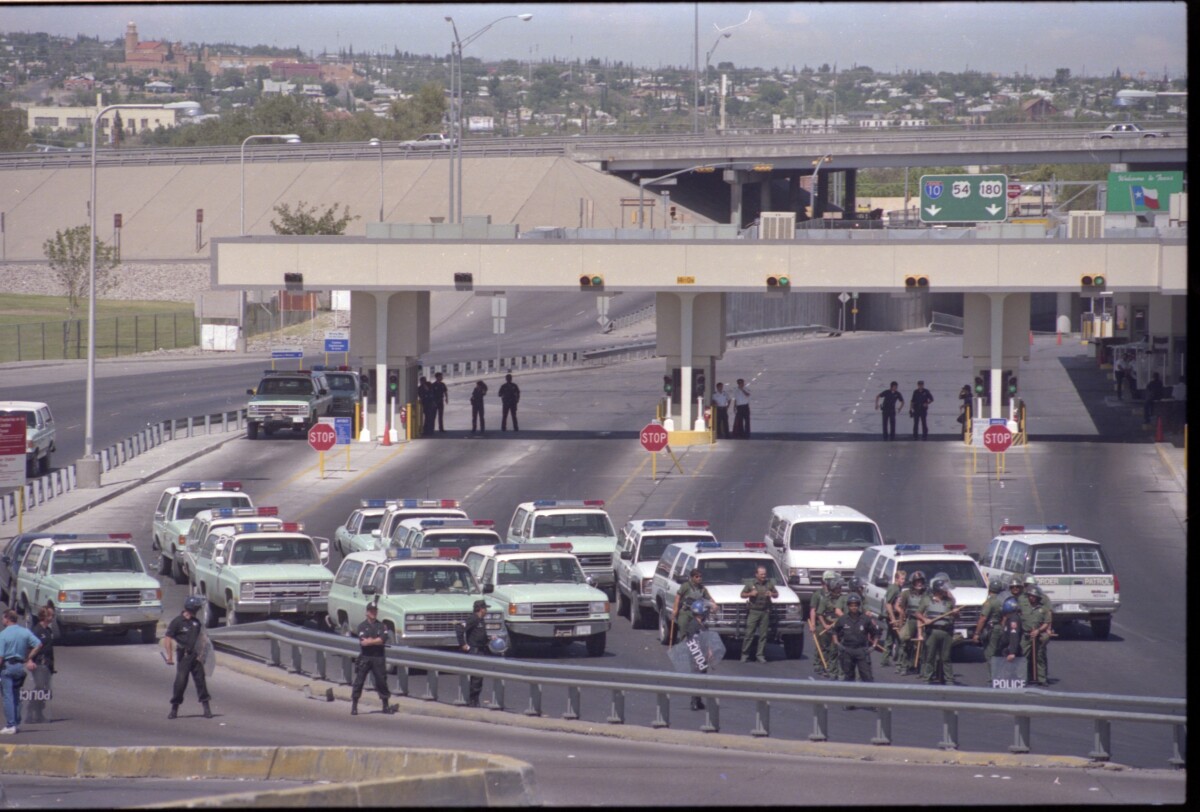
The image shows the U.S. Border Patrol during Operation Hold the Line in 1993. Operation Hold the Line was a preventative measure taken by the United States Border Patrol, initiated on September 19, 1993, on the United States-Mexico border in El Paso. Silvestre Reyes, who was the head of the El Paso Border Control at the time, ordered his officers to form a human and vehicle blockade along the border. There were four hundred agents and vehicles every 100 yards from one side of El Paso to the other, creating a virtual and visible human wall of enforcement, in order to prevent illegal immigration. Unlike the previous attempts, Reyes’ blockade stayed in place until the Immigration and Naturalization Service saw the success it was having and permanently funded it. It is still in effect today. The rise of illegal immigration from Mexico to the U.S. during the 1980s and 1990s was caused by the collapse of the Mexican economy due to inflation. El Paso's Border Patrol agents, which numbered 600 then, were overwhelmed by the number of migrants rushing across the border daily. The Operation was the first of its kind and represented a shift in ideology in policing illegal immigration. Previous policies focused on finding and deporting illegal immigrants who had already crossed the border. Instead, Operation Hold the Line focused on intercepting and preventing illegal entries at the border. The Operation affected El Paso and the surrounding areas instantly and in different ways: On one hand, the apprehensions in the El Paso sector dropped significantly (from about 1,500 people a day to less than 100 a day). The success of the Operation led to the introduction of legislation that focused on border security. On the other hand, the number of immigrants who die trying to cross the border has risen significantly, because they attempt to cross the border in remote desert areas, which have less security. Also, illegal immigrants, who successfully cross the border, stay in the United States longer than before, rather than risking arrest traveling back and forth from Mexico. During the first weeks of the Operation, there were protests on both sides of the border, and the Catholic bishops of Southern New Mexico, El Paso and Juárez came out against it. Hundreds of Juárez residents took part in demonstrations because they could no longer get to their jobs in El Paso. Consequently, one of the immediate effects was also that it left thousands of people from Juarez unemployed, who had been crossing the border daily for their jobs in El Paso. About a week into the operation, there was a standoff between protesters and U.S. officials at the Paso del Norte International Bridge. They threatened to pour into the north, and the Border Patrol had to shut down one side of the bridge.
Reportar esta entrada
Más sobre la misma comunidad-colección
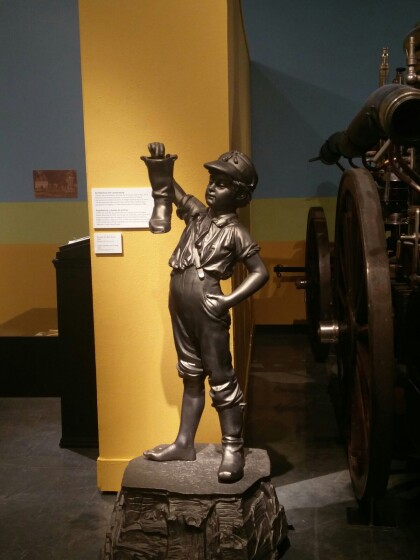
Estatua del Niño con la bota El Paso, Tejas
The Boy was first placed in the park next to old City Hall in ...
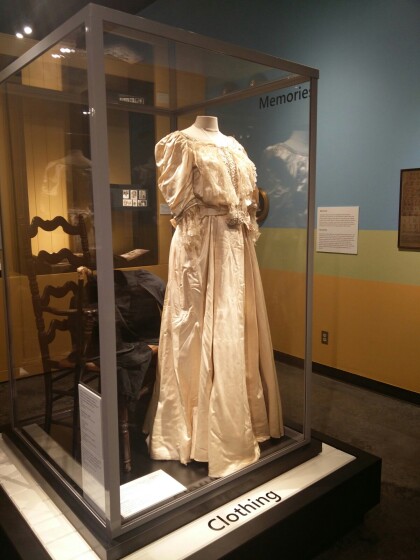
Vestimento de boda de mujer y hombre El Paso, Tejas
Man’s Wedding Coat, 1853 Worn by Prof. C.C. Huffaker at his ...
Arquitectura y Paisajismo El Paso, Tejas
Both the Spanish and the Native American peoples of Meso America ...
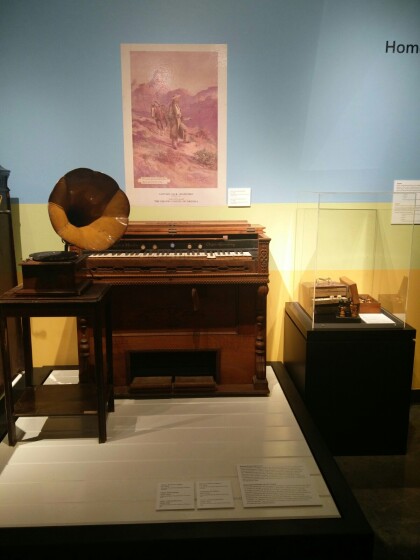
Organó de Mason y Hamlin y Fonógrafo de Edison
Mason & Hamlin Organ, ca. 1870. Edison Phonograph, 1915-1919. ...
Máquinas de escribir y herramientas para hacer silla de montar
Skills Choosing El Paso often meant bringing skills to the ...
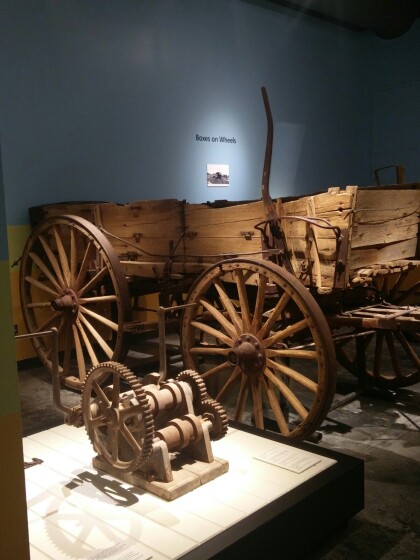
Vagón del ejército y reparación de la rueda
U.S. Army Wagon, ca. 1915 Wrecked during service on the border ...
Gunning Casteel, Inc. El Paso, Tejas
Gunning Casteel was a pharmacy in downtown El Paso, Texas circa ...
Gunning Casteel, inc Receta de Medicamentos El Paso, Tejas
Headache prescription filled by Gunning Casteel pharmacy in El ...
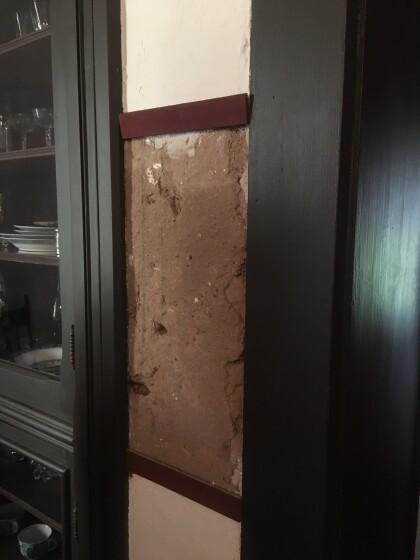
Adobe Original Usado Para El Hogar El Paso, Tejas
Image shows small sample of original adobe used in historic ...
1971 Roxana Angulo - El Paso, Tejas
1971 Roxana Angulo, born to Rosemary Gereda and Jorge I. Angulo, ...