Reportar esta entrada
Más sobre la misma comunidad-colección
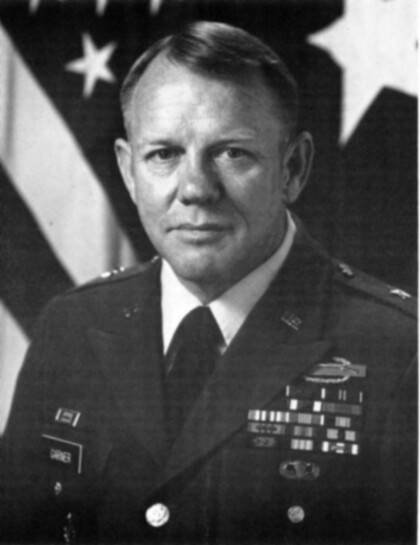
Jay M. Garner - Un Antiguo General Comando en Fort Bliss, Texas
Born in Arcadia, Florida, Garner served an enlistment in the ...
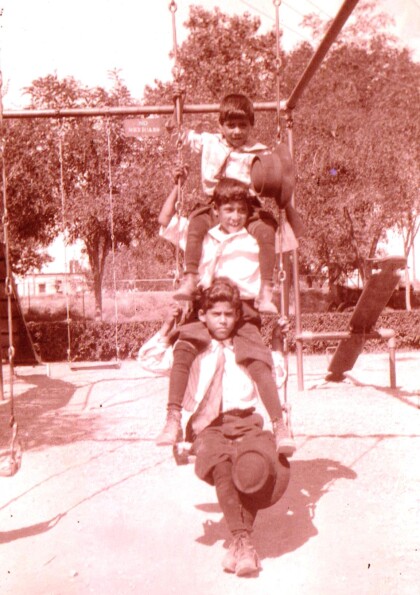
Niños jugando en el columpio en la parque de Washington
Alfredo, Enrique, and Jose, Jr. Berroteran on swing in ...
El tren en el camino a Alamogordo
Since the railroad had been built in El Paso in 1882, the city ...
Inundación en sur de la calle El Paso, 1916
The image shows the flood on South El Paso Street in 1916.
Piscina en Washington Park El Paso, Tejas
This swimming pool was located at Washington Park El Paso Texas ...
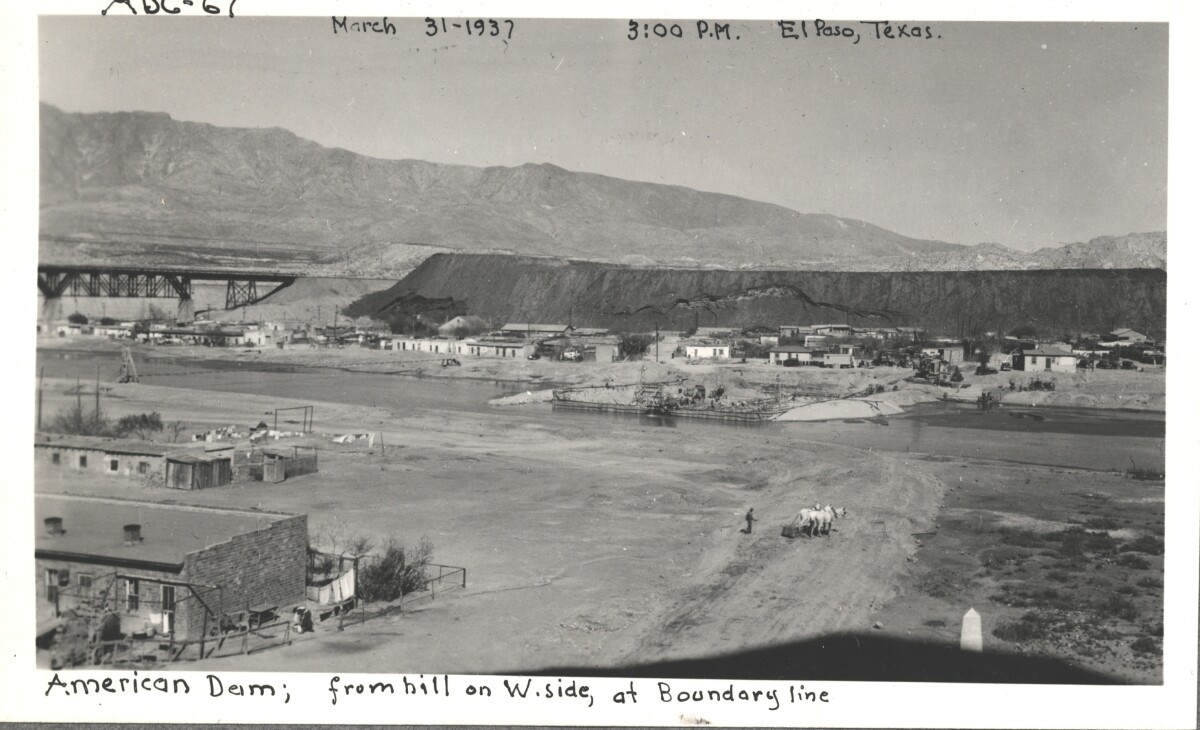
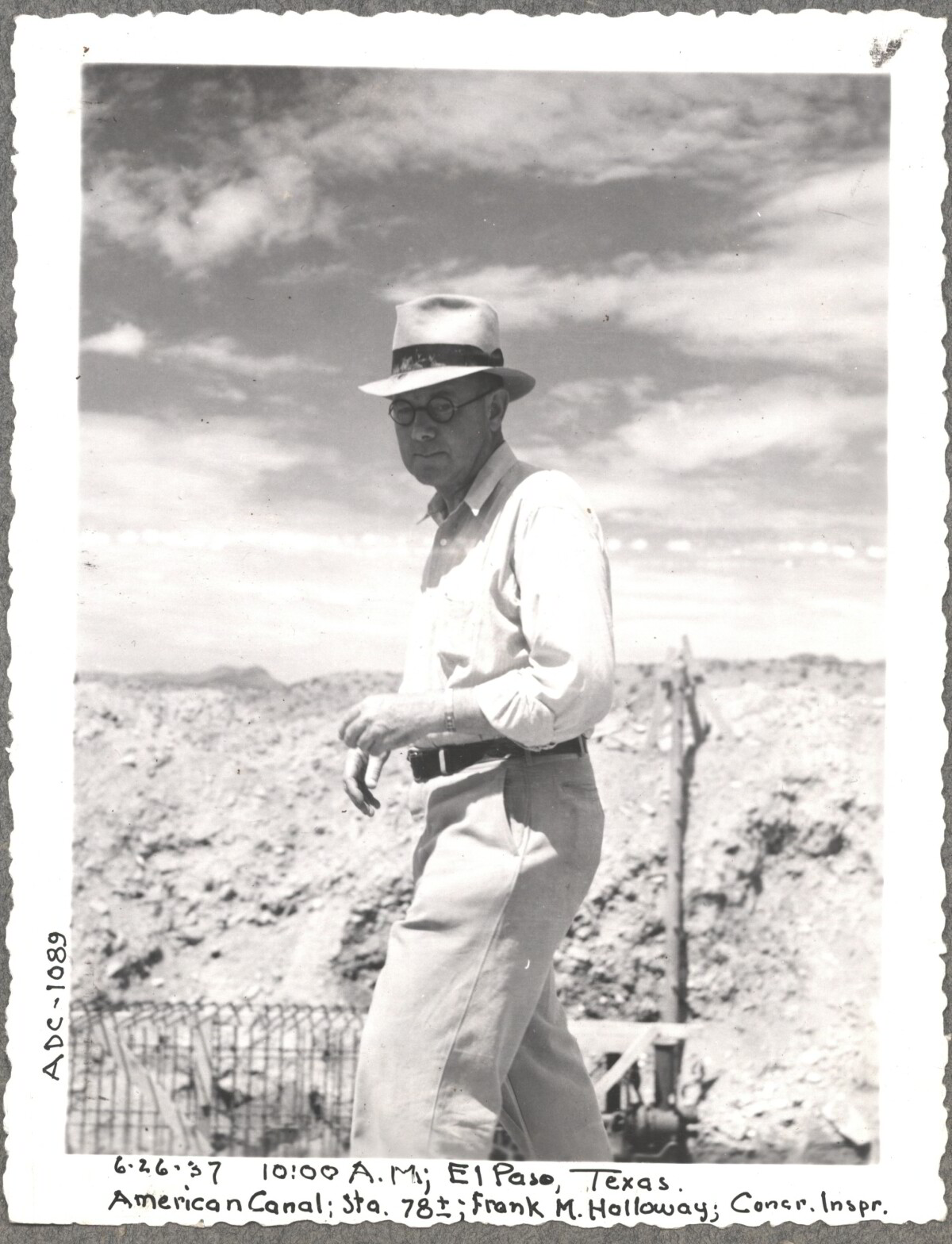
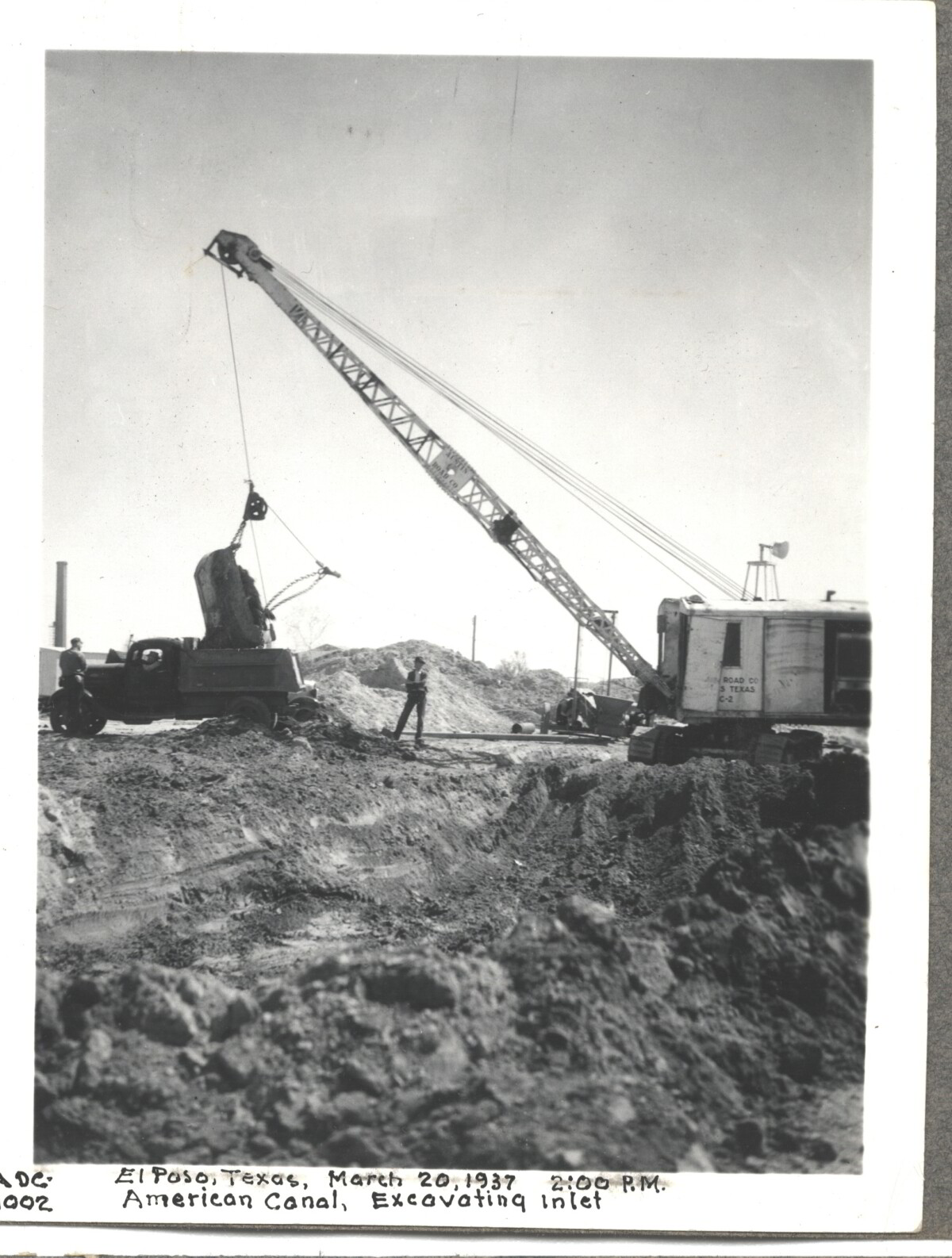
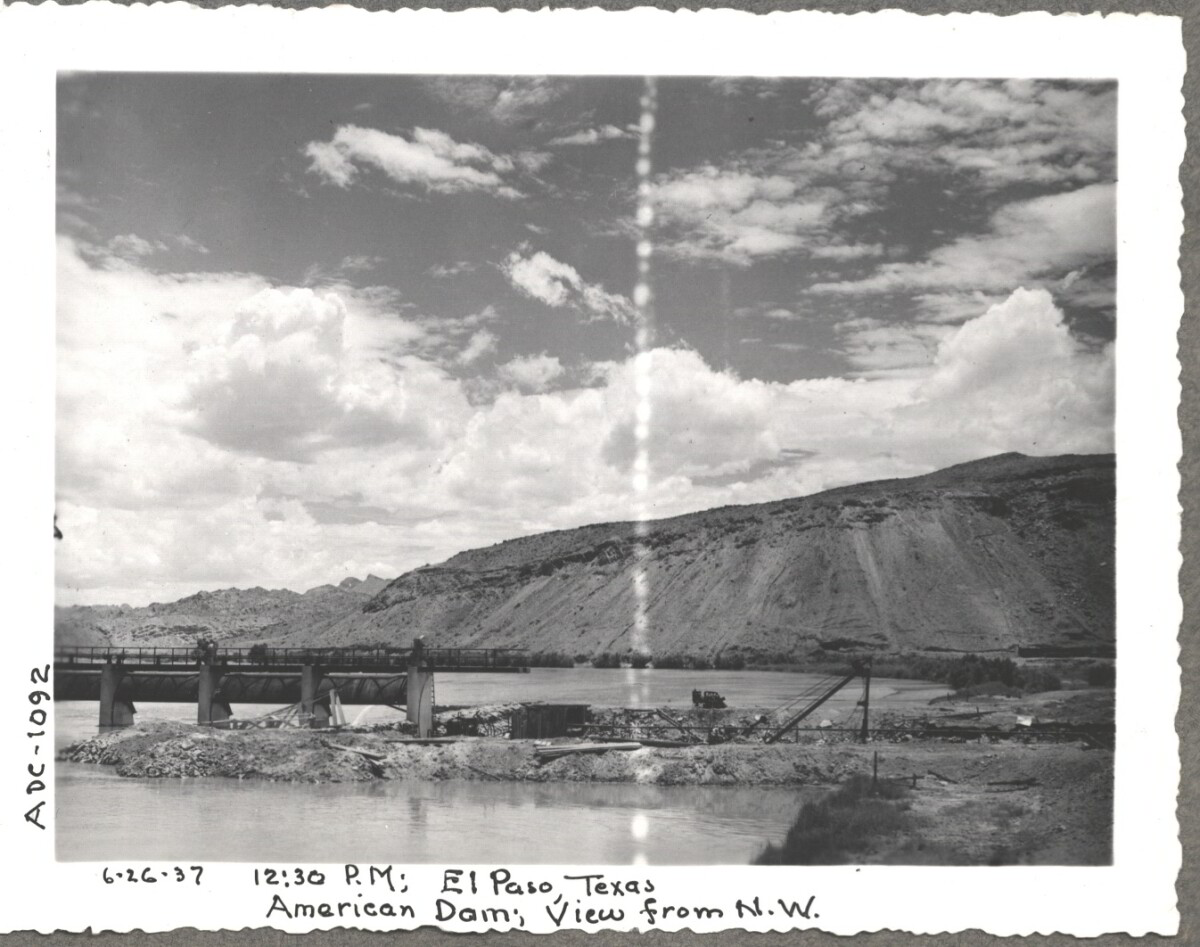






























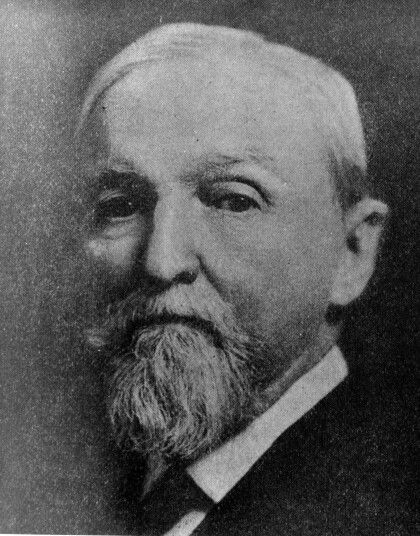









Comentarios
Hacer un comentario