St. Luke's Hospital - El Paso, Texas
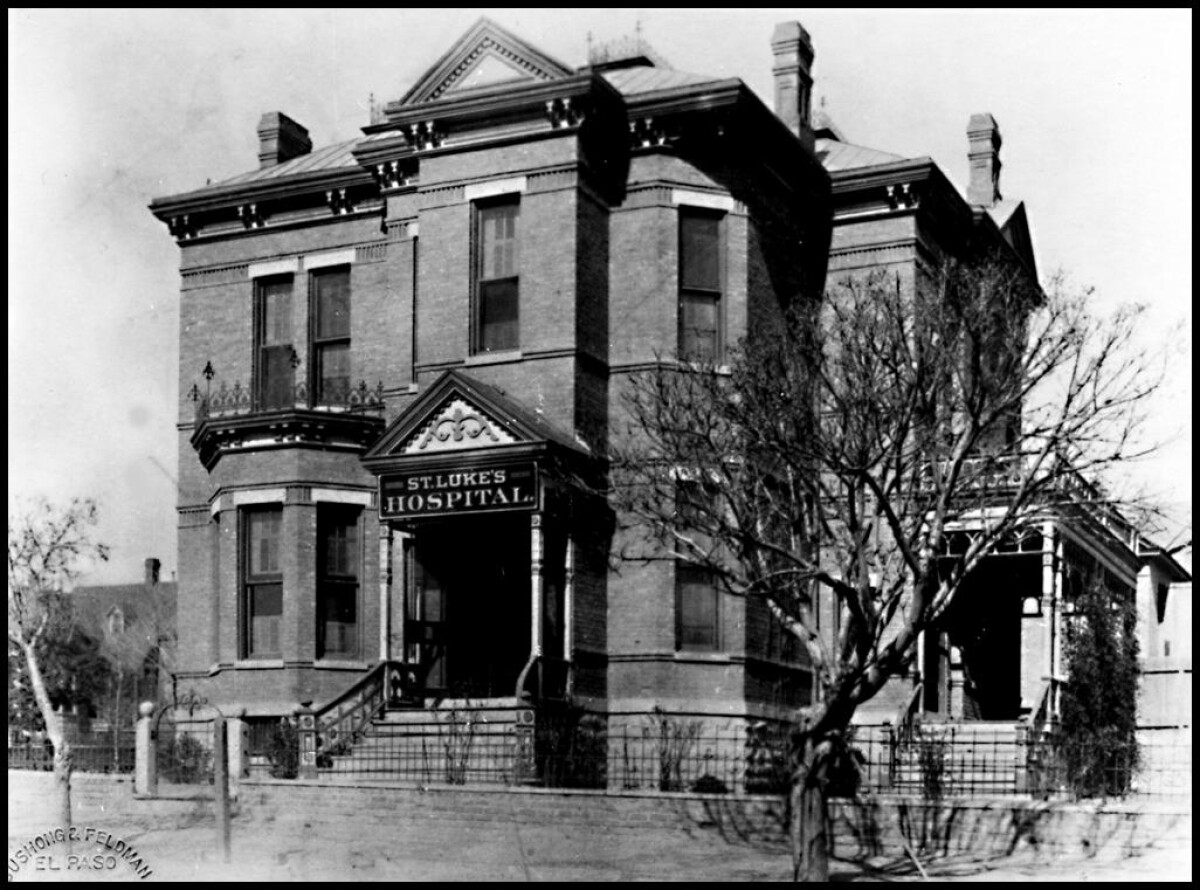

St. Luke's Hospital - El Paso, Texas
The image shows the St. Luke's Hospital in the 1900s. It was one of the first hospitals in town which treated tuberculosis patients. In the late 1800s and early 1900s, tuberculosis spread rapidly in the United States. Throughout most of the 19th century, pulmonary tuberculosis was thought to be a hereditary disease aggravated by humid air, damp soil, lack of exercise, inadequate diet, and overcrowded and poorly ventilated housing. However, in 1882, German physician Robert Koch described the rod-shaped organism called the tubercle bacillus that causes tuberculosis. The microscopic bacteria were impossible to destroy unless exposed to heat or light. Since most infections came from people with pulmonary TB, such people needed to be isolated to check the spread of the disease. The Southwest, including El Paso, was considered ideal for the treatment of TB because of its dry, warm climate. It attracted TB patients from all over the country. The completion of the Southern Pacific Railroad in 1881 encouraged tuberculars to come west. Early care of TB patients consisted of sitting in parks to absorb the sun and convalescence in private homes. This method was ineffective and many people died. The migration of infected persons in search of a climatic cure created a major public health problem for sections of the Southwest from the late 1890s through the 1920s. During this period, many sanatoriums and hospitals opened to treat tuberculars and this deadly disease helped establish El Paso as a health center. Dr. J. Shelton Hoseley opened St. Luke's Hospital at 199 Missouri Street in El Paso, Texas in 1900. He sold it to Dr. Charles B. Hanson in 1903 and then founded another large hospital treating mainly TB patients.
Report this entry
More from the same community-collection
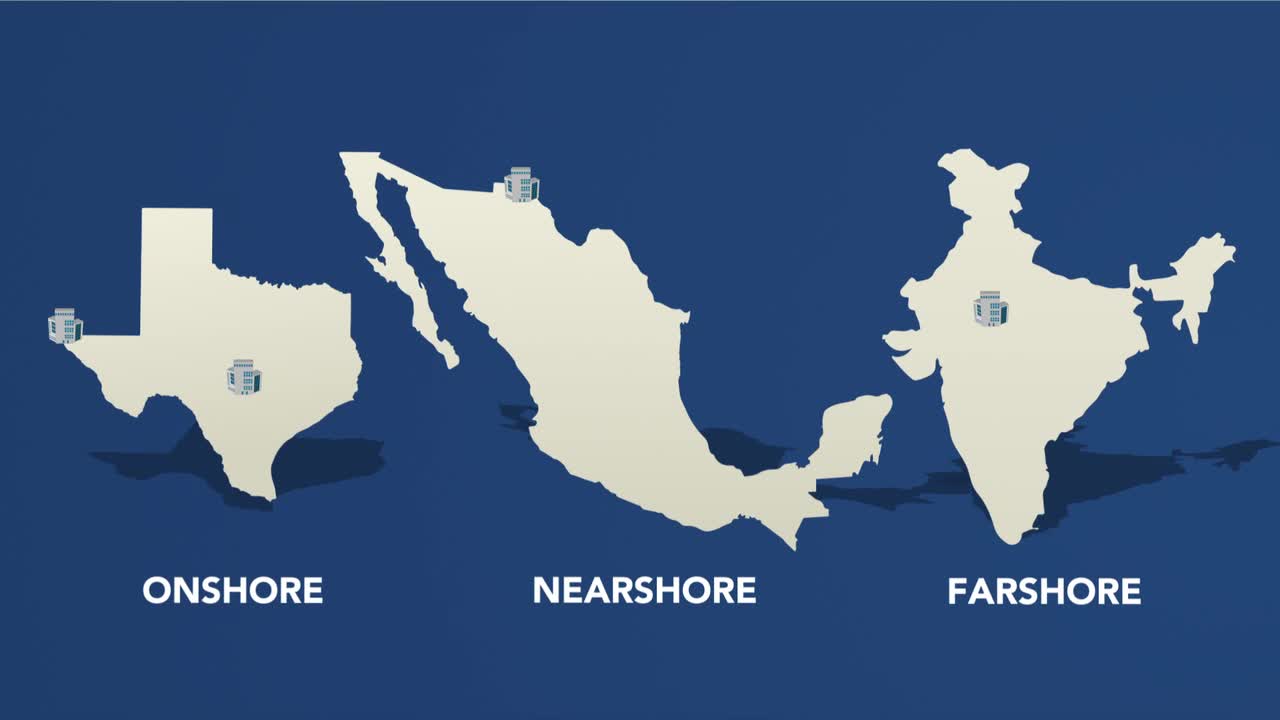
DATAMARK, Inc. Marks 25 Years in Business
Celebrating its 25th year in business in 2015, DATAMARK, Inc. is ...