Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot by Hank Willis Thomas
The past is always present. It is not always visible, but like the molecules that we are composed of, it is everywhere, ever-changing, and always part of us. — Hank Willis Thomas
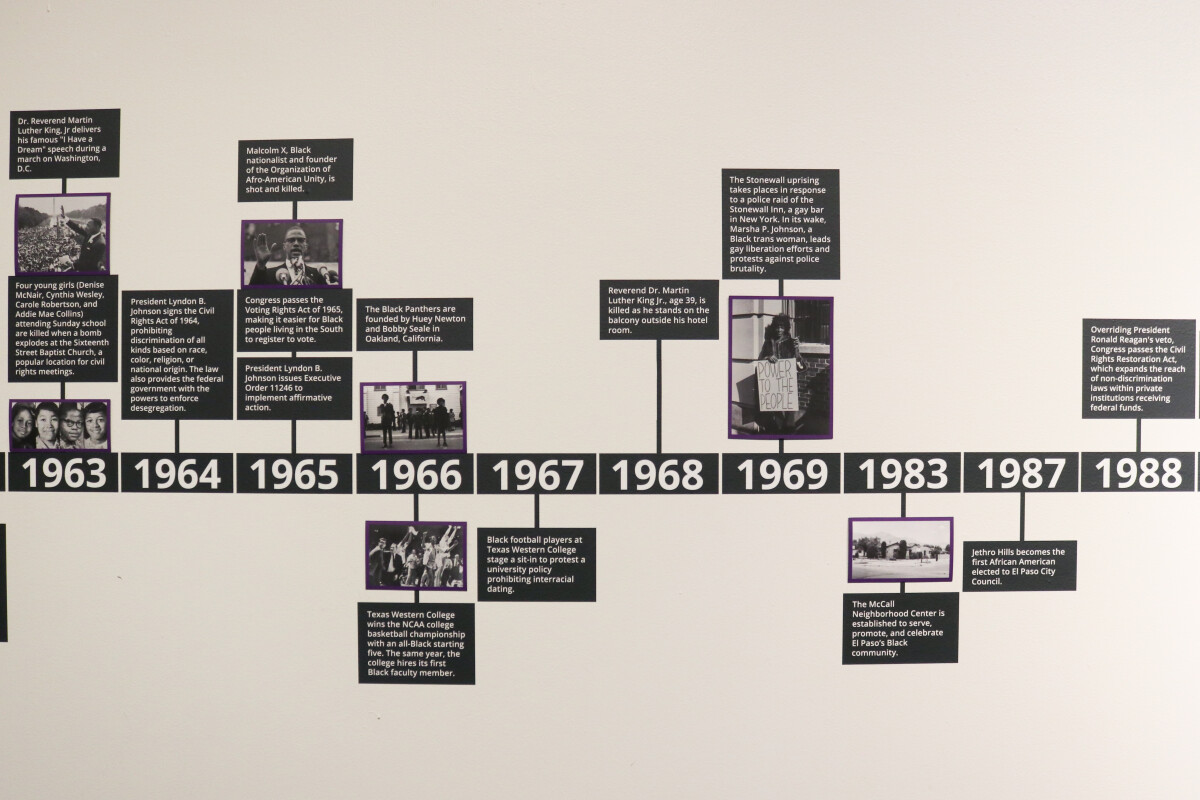
In 2018, the Delaware Art Museum partnered with organizations throughout the city of Wilmington, Delaware to mark 50 years since the powerful and community-changing public response that followed the assassination of Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. on April 4, 1968. Civil disturbances in Wilmington followed by a nine-month-long occupation by the National Guard left an indelible mark on the community. The Museum commissioned artist Hank Willis Thomas to respond to the events of 1968 through the creation of a new work of art that sheds light on this complicated moment in the city’s history. Following the exhibition, the Museum acquired Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot from Thomas for the benefit of the communities it serves.
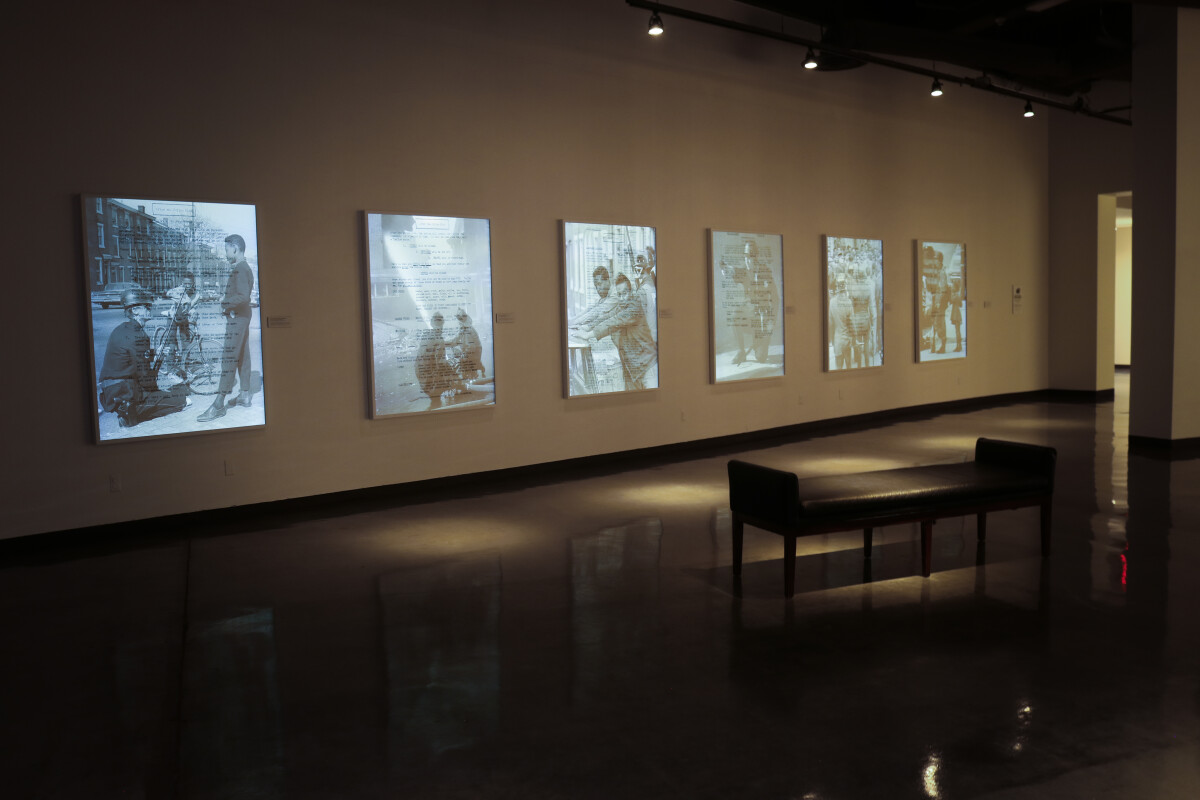
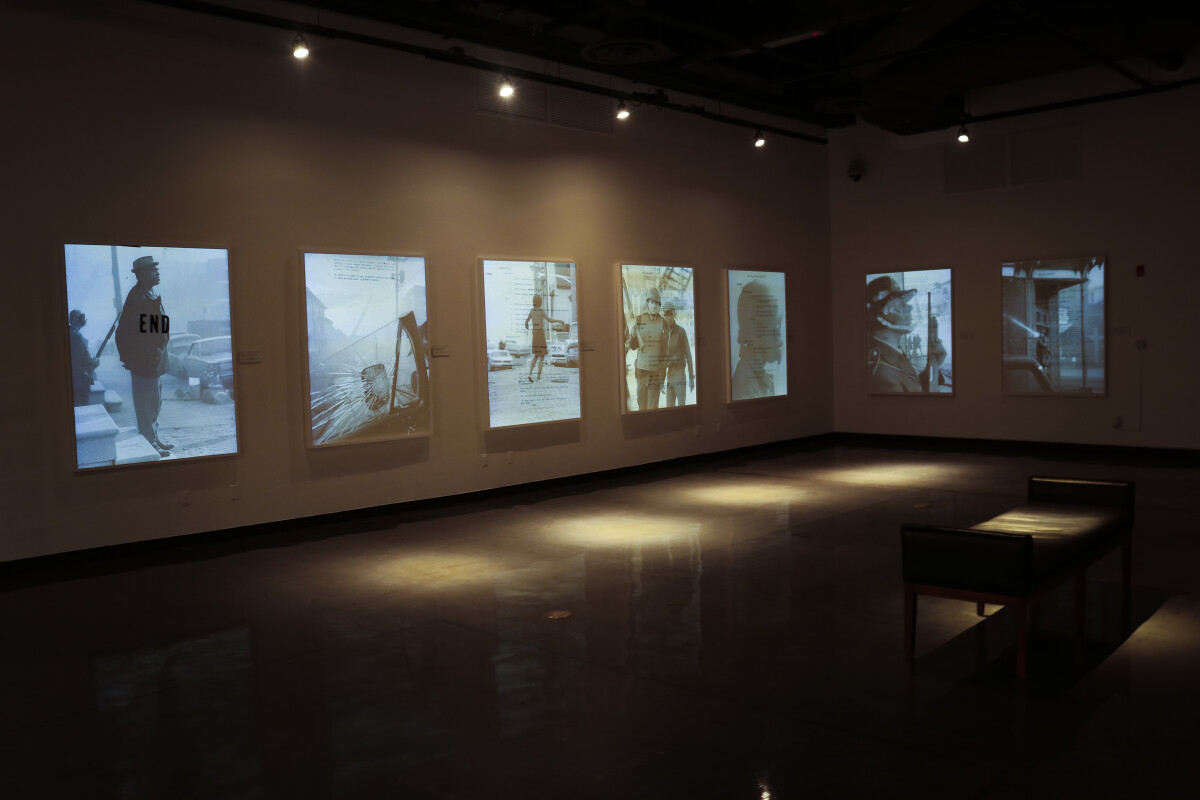
Hank Willis Thomas explores the complexities of race, gender, and class in his photography, sculpture, and video-based artwork. For this project, he combined historic News Journal photographs with the historic pamphlet Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot. Informed by the uprisings of 1967, Cold War-era nuclear fallout pamphlets, and guides published for African Americans to navigate institutional racism during segregations laws, the booklet serves as a practical manual for surviving an occupation. The guide outlines that police and media response will be followed by business closures, electricity outages, and travel restrictions. Provisions—food, water, and basic medical supplies—must be gathered, and those under siege must also know how to provide basic care for medical emergencies.
Thomas created a powerfully unique physical and visual viewing experience by combining image and text on retroreflective vinyl – a material widely used in road signage. The pages of the survival guide are activated when a flash of light catches the News Journal photograph underneath. Events on the verge of being lost to historical amnesia are revealed again. With this rediscovery, the viewer is placed in the position of the many individuals who directly or indirectly experienced these events—city residents, Wilmington firefighters, and National Guardsmen. For Thomas, this is how the past remains current, and how the “holes of narrative history” are exposed.
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot is organized by Deleware Art Museum, Wilmington, Deleware. Support provided by Art Bridges.
Area:
Central / Downtown
Source:
El Paso Museum of History; Delaware Museum of Art; Art Bridges
Uploaded by:
El Paso Museum of History
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot by Hank Willis Thomas
The past is always present. It is not always visible, but like the molecules that we are composed of, it is everywhere, ever-changing, and always part of us. — Hank Willis Thomas
In 2018, the Delaware Art Museum partnered with organizations throughout the city of Wilmington, Delaware to mark 50 years since the powerful and community-changing public response that followed the assassination of Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. on April 4, 1968. Civil disturbances in Wilmington followed by a nine-month-long occupation by the National Guard left an indelible mark on the community. The Museum commissioned artist Hank Willis Thomas to respond to the events of 1968 through the creation of a new work of art that sheds light on this complicated moment in the city’s history. Following the exhibition, the Museum acquired Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot from Thomas for the benefit of the communities it serves.
Hank Willis Thomas explores the complexities of race, gender, and class in his photography, sculpture, and video-based artwork. For this project, he combined historic News Journal photographs with the historic pamphlet Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot. Informed by the uprisings of 1967, Cold War-era nuclear fallout pamphlets, and guides published for African Americans to navigate institutional racism during segregations laws, the booklet serves as a practical manual for surviving an occupation. The guide outlines that police and media response will be followed by business closures, electricity outages, and travel restrictions. Provisions—food, water, and basic medical supplies—must be gathered, and those under siege must also know how to provide basic care for medical emergencies.
Thomas created a powerfully unique physical and visual viewing experience by combining image and text on retroreflective vinyl – a material widely used in road signage. The pages of the survival guide are activated when a flash of light catches the News Journal photograph underneath. Events on the verge of being lost to historical amnesia are revealed again. With this rediscovery, the viewer is placed in the position of the many individuals who directly or indirectly experienced these events—city residents, Wilmington firefighters, and National Guardsmen. For Thomas, this is how the past remains current, and how the “holes of narrative history” are exposed.
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot is organized by Deleware Art Museum, Wilmington, Deleware. Support provided by Art Bridges.
Area:
Central / Downtown
Source:
El Paso Museum of History; Delaware Museum of Art; Art Bridges
Uploaded by:
El Paso Museum of History
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot by Hank Willis Thomas
The past is always present. It is not always visible, but like the molecules that we are composed of, it is everywhere, ever-changing, and always part of us. — Hank Willis Thomas
In 2018, the Delaware Art Museum partnered with organizations throughout the city of Wilmington, Delaware to mark 50 years since the powerful and community-changing public response that followed the assassination of Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. on April 4, 1968. Civil disturbances in Wilmington followed by a nine-month-long occupation by the National Guard left an indelible mark on the community. The Museum commissioned artist Hank Willis Thomas to respond to the events of 1968 through the creation of a new work of art that sheds light on this complicated moment in the city’s history. Following the exhibition, the Museum acquired Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot from Thomas for the benefit of the communities it serves.
Hank Willis Thomas explores the complexities of race, gender, and class in his photography, sculpture, and video-based artwork. For this project, he combined historic News Journal photographs with the historic pamphlet Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot. Informed by the uprisings of 1967, Cold War-era nuclear fallout pamphlets, and guides published for African Americans to navigate institutional racism during segregations laws, the booklet serves as a practical manual for surviving an occupation. The guide outlines that police and media response will be followed by business closures, electricity outages, and travel restrictions. Provisions—food, water, and basic medical supplies—must be gathered, and those under siege must also know how to provide basic care for medical emergencies.
Thomas created a powerfully unique physical and visual viewing experience by combining image and text on retroreflective vinyl – a material widely used in road signage. The pages of the survival guide are activated when a flash of light catches the News Journal photograph underneath. Events on the verge of being lost to historical amnesia are revealed again. With this rediscovery, the viewer is placed in the position of the many individuals who directly or indirectly experienced these events—city residents, Wilmington firefighters, and National Guardsmen. For Thomas, this is how the past remains current, and how the “holes of narrative history” are exposed.
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot is organized by Deleware Art Museum, Wilmington, Deleware. Support provided by Art Bridges.
Area:
Central / Downtown
Source:
El Paso Museum of History; Delaware Museum of Art; Art Bridges
Uploaded by:
El Paso Museum of History
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot by Hank Willis Thomas
The past is always present. It is not always visible, but like the molecules that we are composed of, it is everywhere, ever-changing, and always part of us. — Hank Willis Thomas
In 2018, the Delaware Art Museum partnered with organizations throughout the city of Wilmington, Delaware to mark 50 years since the powerful and community-changing public response that followed the assassination of Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. on April 4, 1968. Civil disturbances in Wilmington followed by a nine-month-long occupation by the National Guard left an indelible mark on the community. The Museum commissioned artist Hank Willis Thomas to respond to the events of 1968 through the creation of a new work of art that sheds light on this complicated moment in the city’s history. Following the exhibition, the Museum acquired Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot from Thomas for the benefit of the communities it serves.
Hank Willis Thomas explores the complexities of race, gender, and class in his photography, sculpture, and video-based artwork. For this project, he combined historic News Journal photographs with the historic pamphlet Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot. Informed by the uprisings of 1967, Cold War-era nuclear fallout pamphlets, and guides published for African Americans to navigate institutional racism during segregations laws, the booklet serves as a practical manual for surviving an occupation. The guide outlines that police and media response will be followed by business closures, electricity outages, and travel restrictions. Provisions—food, water, and basic medical supplies—must be gathered, and those under siege must also know how to provide basic care for medical emergencies.
Thomas created a powerfully unique physical and visual viewing experience by combining image and text on retroreflective vinyl – a material widely used in road signage. The pages of the survival guide are activated when a flash of light catches the News Journal photograph underneath. Events on the verge of being lost to historical amnesia are revealed again. With this rediscovery, the viewer is placed in the position of the many individuals who directly or indirectly experienced these events—city residents, Wilmington firefighters, and National Guardsmen. For Thomas, this is how the past remains current, and how the “holes of narrative history” are exposed.
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot is organized by Deleware Art Museum, Wilmington, Deleware. Support provided by Art Bridges.
Area:
Central / Downtown
Source:
El Paso Museum of History; Delaware Museum of Art; Art Bridges
Uploaded by:
El Paso Museum of History
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot by Hank Willis Thomas
The past is always present. It is not always visible, but like the molecules that we are composed of, it is everywhere, ever-changing, and always part of us. — Hank Willis Thomas
In 2018, the Delaware Art Museum partnered with organizations throughout the city of Wilmington, Delaware to mark 50 years since the powerful and community-changing public response that followed the assassination of Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. on April 4, 1968. Civil disturbances in Wilmington followed by a nine-month-long occupation by the National Guard left an indelible mark on the community. The Museum commissioned artist Hank Willis Thomas to respond to the events of 1968 through the creation of a new work of art that sheds light on this complicated moment in the city’s history. Following the exhibition, the Museum acquired Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot from Thomas for the benefit of the communities it serves.
Hank Willis Thomas explores the complexities of race, gender, and class in his photography, sculpture, and video-based artwork. For this project, he combined historic News Journal photographs with the historic pamphlet Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot. Informed by the uprisings of 1967, Cold War-era nuclear fallout pamphlets, and guides published for African Americans to navigate institutional racism during segregations laws, the booklet serves as a practical manual for surviving an occupation. The guide outlines that police and media response will be followed by business closures, electricity outages, and travel restrictions. Provisions—food, water, and basic medical supplies—must be gathered, and those under siege must also know how to provide basic care for medical emergencies.
Thomas created a powerfully unique physical and visual viewing experience by combining image and text on retroreflective vinyl – a material widely used in road signage. The pages of the survival guide are activated when a flash of light catches the News Journal photograph underneath. Events on the verge of being lost to historical amnesia are revealed again. With this rediscovery, the viewer is placed in the position of the many individuals who directly or indirectly experienced these events—city residents, Wilmington firefighters, and National Guardsmen. For Thomas, this is how the past remains current, and how the “holes of narrative history” are exposed.
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot is organized by Deleware Art Museum, Wilmington, Deleware. Support provided by Art Bridges.
Area:
Central / Downtown
Source:
El Paso Museum of History; Delaware Museum of Art; Art Bridges
Uploaded by:
El Paso Museum of History
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot by Hank Willis Thomas
The past is always present. It is not always visible, but like the molecules that we are composed of, it is everywhere, ever-changing, and always part of us. — Hank Willis Thomas
In 2018, the Delaware Art Museum partnered with organizations throughout the city of Wilmington, Delaware to mark 50 years since the powerful and community-changing public response that followed the assassination of Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. on April 4, 1968. Civil disturbances in Wilmington followed by a nine-month-long occupation by the National Guard left an indelible mark on the community. The Museum commissioned artist Hank Willis Thomas to respond to the events of 1968 through the creation of a new work of art that sheds light on this complicated moment in the city’s history. Following the exhibition, the Museum acquired Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot from Thomas for the benefit of the communities it serves.
Hank Willis Thomas explores the complexities of race, gender, and class in his photography, sculpture, and video-based artwork. For this project, he combined historic News Journal photographs with the historic pamphlet Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot. Informed by the uprisings of 1967, Cold War-era nuclear fallout pamphlets, and guides published for African Americans to navigate institutional racism during segregations laws, the booklet serves as a practical manual for surviving an occupation. The guide outlines that police and media response will be followed by business closures, electricity outages, and travel restrictions. Provisions—food, water, and basic medical supplies—must be gathered, and those under siege must also know how to provide basic care for medical emergencies.
Thomas created a powerfully unique physical and visual viewing experience by combining image and text on retroreflective vinyl – a material widely used in road signage. The pages of the survival guide are activated when a flash of light catches the News Journal photograph underneath. Events on the verge of being lost to historical amnesia are revealed again. With this rediscovery, the viewer is placed in the position of the many individuals who directly or indirectly experienced these events—city residents, Wilmington firefighters, and National Guardsmen. For Thomas, this is how the past remains current, and how the “holes of narrative history” are exposed.
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot is organized by Deleware Art Museum, Wilmington, Deleware. Support provided by Art Bridges.
Area:
Central / Downtown
Source:
El Paso Museum of History; Delaware Museum of Art; Art Bridges
Uploaded by:
El Paso Museum of History
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot by Hank Willis Thomas
The past is always present. It is not always visible, but like the molecules that we are composed of, it is everywhere, ever-changing, and always part of us. — Hank Willis Thomas
In 2018, the Delaware Art Museum partnered with organizations throughout the city of Wilmington, Delaware to mark 50 years since the powerful and community-changing public response that followed the assassination of Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. on April 4, 1968. Civil disturbances in Wilmington followed by a nine-month-long occupation by the National Guard left an indelible mark on the community. The Museum commissioned artist Hank Willis Thomas to respond to the events of 1968 through the creation of a new work of art that sheds light on this complicated moment in the city’s history. Following the exhibition, the Museum acquired Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot from Thomas for the benefit of the communities it serves.
Hank Willis Thomas explores the complexities of race, gender, and class in his photography, sculpture, and video-based artwork. For this project, he combined historic News Journal photographs with the historic pamphlet Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot. Informed by the uprisings of 1967, Cold War-era nuclear fallout pamphlets, and guides published for African Americans to navigate institutional racism during segregations laws, the booklet serves as a practical manual for surviving an occupation. The guide outlines that police and media response will be followed by business closures, electricity outages, and travel restrictions. Provisions—food, water, and basic medical supplies—must be gathered, and those under siege must also know how to provide basic care for medical emergencies.
Thomas created a powerfully unique physical and visual viewing experience by combining image and text on retroreflective vinyl – a material widely used in road signage. The pages of the survival guide are activated when a flash of light catches the News Journal photograph underneath. Events on the verge of being lost to historical amnesia are revealed again. With this rediscovery, the viewer is placed in the position of the many individuals who directly or indirectly experienced these events—city residents, Wilmington firefighters, and National Guardsmen. For Thomas, this is how the past remains current, and how the “holes of narrative history” are exposed.
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot is organized by Deleware Art Museum, Wilmington, Deleware. Support provided by Art Bridges.
Area:
Central / Downtown
Source:
El Paso Museum of History; Delaware Museum of Art; Art Bridges
Uploaded by:
El Paso Museum of History
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot by Hank Willis Thomas
The past is always present. It is not always visible, but like the molecules that we are composed of, it is everywhere, ever-changing, and always part of us. — Hank Willis Thomas
In 2018, the Delaware Art Museum partnered with organizations throughout the city of Wilmington, Delaware to mark 50 years since the powerful and community-changing public response that followed the assassination of Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. on April 4, 1968. Civil disturbances in Wilmington followed by a nine-month-long occupation by the National Guard left an indelible mark on the community. The Museum commissioned artist Hank Willis Thomas to respond to the events of 1968 through the creation of a new work of art that sheds light on this complicated moment in the city’s history. Following the exhibition, the Museum acquired Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot from Thomas for the benefit of the communities it serves.
Hank Willis Thomas explores the complexities of race, gender, and class in his photography, sculpture, and video-based artwork. For this project, he combined historic News Journal photographs with the historic pamphlet Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot. Informed by the uprisings of 1967, Cold War-era nuclear fallout pamphlets, and guides published for African Americans to navigate institutional racism during segregations laws, the booklet serves as a practical manual for surviving an occupation. The guide outlines that police and media response will be followed by business closures, electricity outages, and travel restrictions. Provisions—food, water, and basic medical supplies—must be gathered, and those under siege must also know how to provide basic care for medical emergencies.
Thomas created a powerfully unique physical and visual viewing experience by combining image and text on retroreflective vinyl – a material widely used in road signage. The pages of the survival guide are activated when a flash of light catches the News Journal photograph underneath. Events on the verge of being lost to historical amnesia are revealed again. With this rediscovery, the viewer is placed in the position of the many individuals who directly or indirectly experienced these events—city residents, Wilmington firefighters, and National Guardsmen. For Thomas, this is how the past remains current, and how the “holes of narrative history” are exposed.
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot is organized by Deleware Art Museum, Wilmington, Deleware. Support provided by Art Bridges.
Area:
Central / Downtown
Source:
El Paso Museum of History; Delaware Museum of Art; Art Bridges
Uploaded by:
El Paso Museum of History
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot by Hank Willis Thomas
The past is always present. It is not always visible, but like the molecules that we are composed of, it is everywhere, ever-changing, and always part of us. — Hank Willis Thomas
In 2018, the Delaware Art Museum partnered with organizations throughout the city of Wilmington, Delaware to mark 50 years since the powerful and community-changing public response that followed the assassination of Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. on April 4, 1968. Civil disturbances in Wilmington followed by a nine-month-long occupation by the National Guard left an indelible mark on the community. The Museum commissioned artist Hank Willis Thomas to respond to the events of 1968 through the creation of a new work of art that sheds light on this complicated moment in the city’s history. Following the exhibition, the Museum acquired Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot from Thomas for the benefit of the communities it serves.
Hank Willis Thomas explores the complexities of race, gender, and class in his photography, sculpture, and video-based artwork. For this project, he combined historic News Journal photographs with the historic pamphlet Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot. Informed by the uprisings of 1967, Cold War-era nuclear fallout pamphlets, and guides published for African Americans to navigate institutional racism during segregations laws, the booklet serves as a practical manual for surviving an occupation. The guide outlines that police and media response will be followed by business closures, electricity outages, and travel restrictions. Provisions—food, water, and basic medical supplies—must be gathered, and those under siege must also know how to provide basic care for medical emergencies.
Thomas created a powerfully unique physical and visual viewing experience by combining image and text on retroreflective vinyl – a material widely used in road signage. The pages of the survival guide are activated when a flash of light catches the News Journal photograph underneath. Events on the verge of being lost to historical amnesia are revealed again. With this rediscovery, the viewer is placed in the position of the many individuals who directly or indirectly experienced these events—city residents, Wilmington firefighters, and National Guardsmen. For Thomas, this is how the past remains current, and how the “holes of narrative history” are exposed.
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot is organized by Deleware Art Museum, Wilmington, Deleware. Support provided by Art Bridges.
Area:
Central / Downtown
Source:
El Paso Museum of History; Delaware Museum of Art; Art Bridges
Uploaded by:
El Paso Museum of History
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot by Hank Willis Thomas
The past is always present. It is not always visible, but like the molecules that we are composed of, it is everywhere, ever-changing, and always part of us. — Hank Willis Thomas
In 2018, the Delaware Art Museum partnered with organizations throughout the city of Wilmington, Delaware to mark 50 years since the powerful and community-changing public response that followed the assassination of Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. on April 4, 1968. Civil disturbances in Wilmington followed by a nine-month-long occupation by the National Guard left an indelible mark on the community. The Museum commissioned artist Hank Willis Thomas to respond to the events of 1968 through the creation of a new work of art that sheds light on this complicated moment in the city’s history. Following the exhibition, the Museum acquired Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot from Thomas for the benefit of the communities it serves.
Hank Willis Thomas explores the complexities of race, gender, and class in his photography, sculpture, and video-based artwork. For this project, he combined historic News Journal photographs with the historic pamphlet Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot. Informed by the uprisings of 1967, Cold War-era nuclear fallout pamphlets, and guides published for African Americans to navigate institutional racism during segregations laws, the booklet serves as a practical manual for surviving an occupation. The guide outlines that police and media response will be followed by business closures, electricity outages, and travel restrictions. Provisions—food, water, and basic medical supplies—must be gathered, and those under siege must also know how to provide basic care for medical emergencies.
Thomas created a powerfully unique physical and visual viewing experience by combining image and text on retroreflective vinyl – a material widely used in road signage. The pages of the survival guide are activated when a flash of light catches the News Journal photograph underneath. Events on the verge of being lost to historical amnesia are revealed again. With this rediscovery, the viewer is placed in the position of the many individuals who directly or indirectly experienced these events—city residents, Wilmington firefighters, and National Guardsmen. For Thomas, this is how the past remains current, and how the “holes of narrative history” are exposed.
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot is organized by Deleware Art Museum, Wilmington, Deleware. Support provided by Art Bridges.
Area:
Central / Downtown
Source:
El Paso Museum of History; Delaware Museum of Art; Art Bridges
Uploaded by:
El Paso Museum of History
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot by Hank Willis Thomas
The past is always present. It is not always visible, but like the molecules that we are composed of, it is everywhere, ever-changing, and always part of us. — Hank Willis Thomas
In 2018, the Delaware Art Museum partnered with organizations throughout the city of Wilmington, Delaware to mark 50 years since the powerful and community-changing public response that followed the assassination of Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. on April 4, 1968. Civil disturbances in Wilmington followed by a nine-month-long occupation by the National Guard left an indelible mark on the community. The Museum commissioned artist Hank Willis Thomas to respond to the events of 1968 through the creation of a new work of art that sheds light on this complicated moment in the city’s history. Following the exhibition, the Museum acquired Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot from Thomas for the benefit of the communities it serves.
Hank Willis Thomas explores the complexities of race, gender, and class in his photography, sculpture, and video-based artwork. For this project, he combined historic News Journal photographs with the historic pamphlet Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot. Informed by the uprisings of 1967, Cold War-era nuclear fallout pamphlets, and guides published for African Americans to navigate institutional racism during segregations laws, the booklet serves as a practical manual for surviving an occupation. The guide outlines that police and media response will be followed by business closures, electricity outages, and travel restrictions. Provisions—food, water, and basic medical supplies—must be gathered, and those under siege must also know how to provide basic care for medical emergencies.
Thomas created a powerfully unique physical and visual viewing experience by combining image and text on retroreflective vinyl – a material widely used in road signage. The pages of the survival guide are activated when a flash of light catches the News Journal photograph underneath. Events on the verge of being lost to historical amnesia are revealed again. With this rediscovery, the viewer is placed in the position of the many individuals who directly or indirectly experienced these events—city residents, Wilmington firefighters, and National Guardsmen. For Thomas, this is how the past remains current, and how the “holes of narrative history” are exposed.
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot is organized by Deleware Art Museum, Wilmington, Deleware. Support provided by Art Bridges.
Area:
Central / Downtown
Source:
El Paso Museum of History; Delaware Museum of Art; Art Bridges
Uploaded by:
El Paso Museum of History
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot by Hank Willis Thomas
The past is always present. It is not always visible, but like the molecules that we are composed of, it is everywhere, ever-changing, and always part of us. — Hank Willis Thomas
In 2018, the Delaware Art Museum partnered with organizations throughout the city of Wilmington, Delaware to mark 50 years since the powerful and community-changing public response that followed the assassination of Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. on April 4, 1968. Civil disturbances in Wilmington followed by a nine-month-long occupation by the National Guard left an indelible mark on the community. The Museum commissioned artist Hank Willis Thomas to respond to the events of 1968 through the creation of a new work of art that sheds light on this complicated moment in the city’s history. Following the exhibition, the Museum acquired Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot from Thomas for the benefit of the communities it serves.
Hank Willis Thomas explores the complexities of race, gender, and class in his photography, sculpture, and video-based artwork. For this project, he combined historic News Journal photographs with the historic pamphlet Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot. Informed by the uprisings of 1967, Cold War-era nuclear fallout pamphlets, and guides published for African Americans to navigate institutional racism during segregations laws, the booklet serves as a practical manual for surviving an occupation. The guide outlines that police and media response will be followed by business closures, electricity outages, and travel restrictions. Provisions—food, water, and basic medical supplies—must be gathered, and those under siege must also know how to provide basic care for medical emergencies.
Thomas created a powerfully unique physical and visual viewing experience by combining image and text on retroreflective vinyl – a material widely used in road signage. The pages of the survival guide are activated when a flash of light catches the News Journal photograph underneath. Events on the verge of being lost to historical amnesia are revealed again. With this rediscovery, the viewer is placed in the position of the many individuals who directly or indirectly experienced these events—city residents, Wilmington firefighters, and National Guardsmen. For Thomas, this is how the past remains current, and how the “holes of narrative history” are exposed.
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot is organized by Deleware Art Museum, Wilmington, Deleware. Support provided by Art Bridges.
Area:
Central / Downtown
Source:
El Paso Museum of History; Delaware Museum of Art; Art Bridges
Uploaded by:
El Paso Museum of History
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot by Hank Willis Thomas
The past is always present. It is not always visible, but like the molecules that we are composed of, it is everywhere, ever-changing, and always part of us. — Hank Willis Thomas
In 2018, the Delaware Art Museum partnered with organizations throughout the city of Wilmington, Delaware to mark 50 years since the powerful and community-changing public response that followed the assassination of Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. on April 4, 1968. Civil disturbances in Wilmington followed by a nine-month-long occupation by the National Guard left an indelible mark on the community. The Museum commissioned artist Hank Willis Thomas to respond to the events of 1968 through the creation of a new work of art that sheds light on this complicated moment in the city’s history. Following the exhibition, the Museum acquired Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot from Thomas for the benefit of the communities it serves.
Hank Willis Thomas explores the complexities of race, gender, and class in his photography, sculpture, and video-based artwork. For this project, he combined historic News Journal photographs with the historic pamphlet Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot. Informed by the uprisings of 1967, Cold War-era nuclear fallout pamphlets, and guides published for African Americans to navigate institutional racism during segregations laws, the booklet serves as a practical manual for surviving an occupation. The guide outlines that police and media response will be followed by business closures, electricity outages, and travel restrictions. Provisions—food, water, and basic medical supplies—must be gathered, and those under siege must also know how to provide basic care for medical emergencies.
Thomas created a powerfully unique physical and visual viewing experience by combining image and text on retroreflective vinyl – a material widely used in road signage. The pages of the survival guide are activated when a flash of light catches the News Journal photograph underneath. Events on the verge of being lost to historical amnesia are revealed again. With this rediscovery, the viewer is placed in the position of the many individuals who directly or indirectly experienced these events—city residents, Wilmington firefighters, and National Guardsmen. For Thomas, this is how the past remains current, and how the “holes of narrative history” are exposed.
Black Survival Guide, or How to Live Through a Police Riot is organized by Deleware Art Museum, Wilmington, Deleware. Support provided by Art Bridges.
Area:
Central / Downtown
Source:
El Paso Museum of History; Delaware Museum of Art; Art Bridges
Uploaded by:
El Paso Museum of History



































Comments
Add a comment