Report this entry
More from the same community-collection
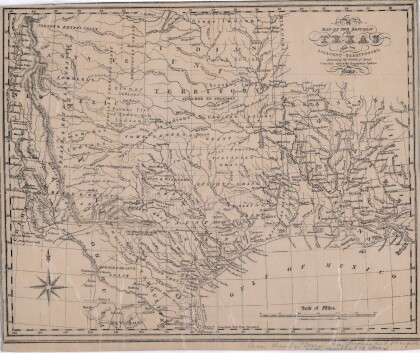
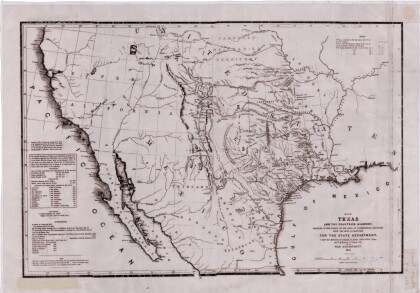
Map of the Republic of Texas and the Adjacent Territories
Map of the Republic of Texas and adjacent territories indicating ...
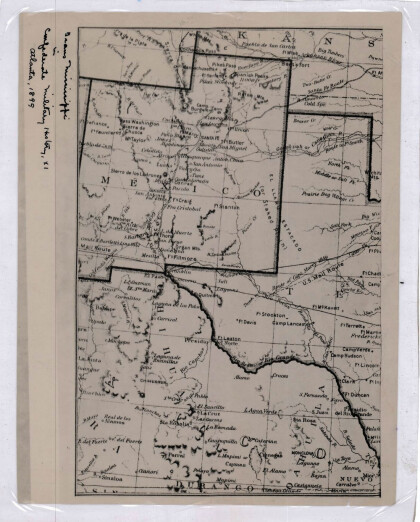
New Mexico, Texas; Chihuahua, Mexico 1861-1865
Map of the borders between New Mexico, Texas and Chihuahua, ...
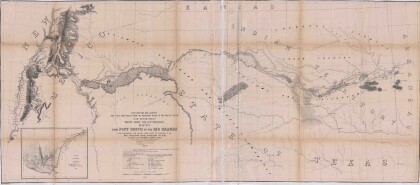
Map No. 1 from Fort Smith to the Rio Grande
Map of the route near the 35th parallel. Part of the ...
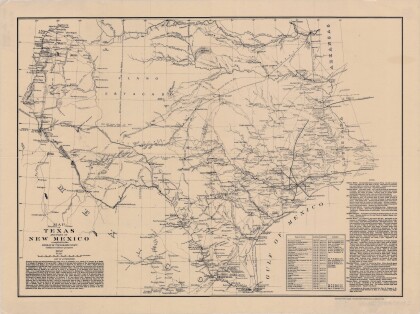
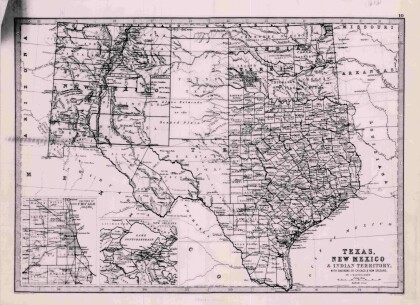
Texas, New Mexico, and Indian Territory
Map of Texas counties and New Mexico showing Indian Territories ...
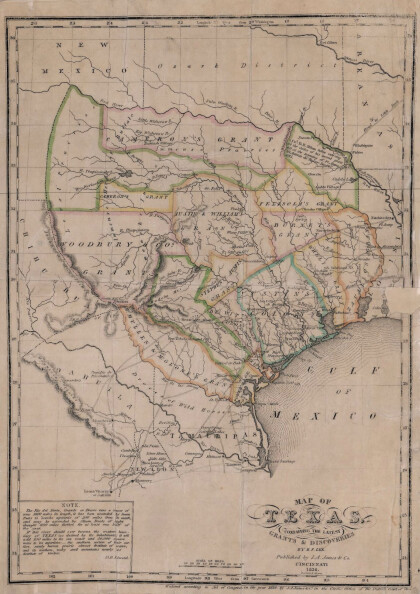
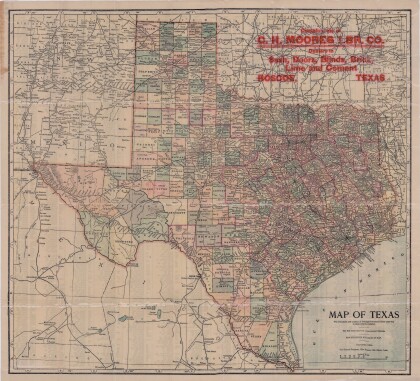
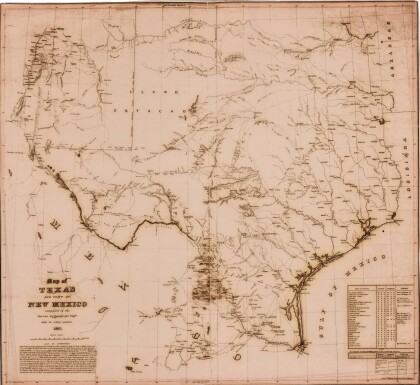
Texas: Containing the Latest Grants and Discoveries
Map of Texas containing the latest grants and discoveries in ...
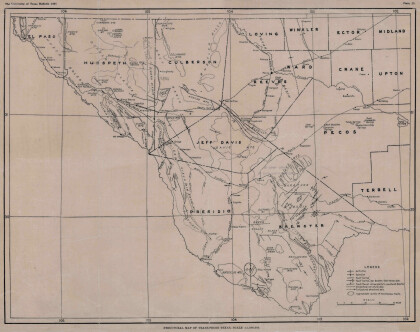
Structural Map of Trans-Pecos Texas
Map of the Trans-Pecos, Texas area; Outlines and lines are shown ...
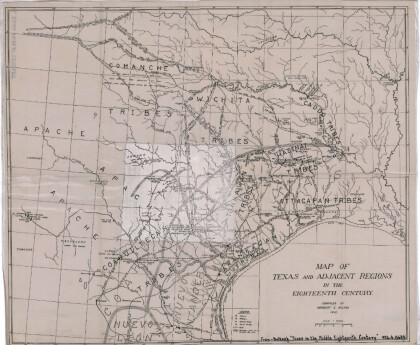
Map of Texas and Adjacent Regions in the Eighteenth Century
Map of Texas and the adjacent regions illustrating missions, ...
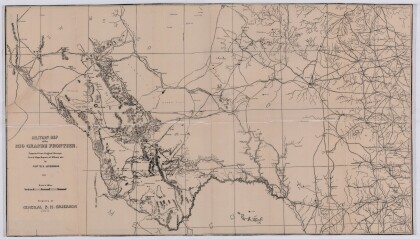
Military Map of the Rio Grande Frontier
Military map of the Rio Grande frontier prepared from original ...
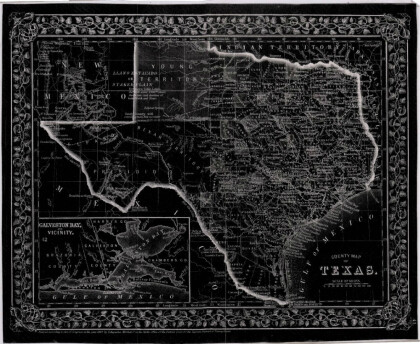
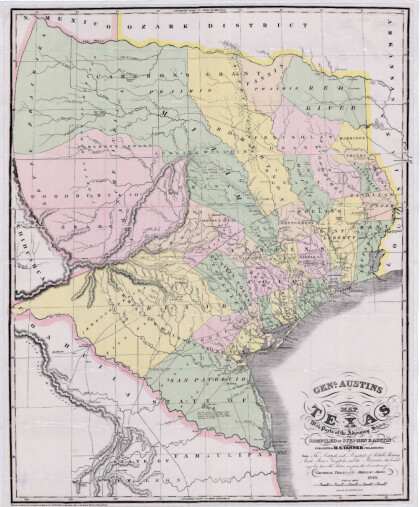
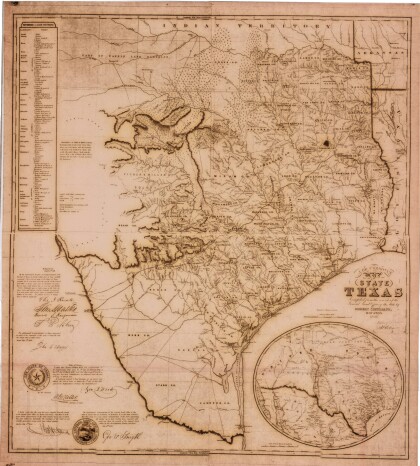
General Austin's Map of Texas with Parts of the Adjoining States
Colorful map of Texas highlighting the borders between states ...
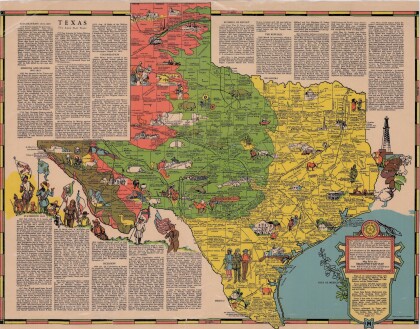
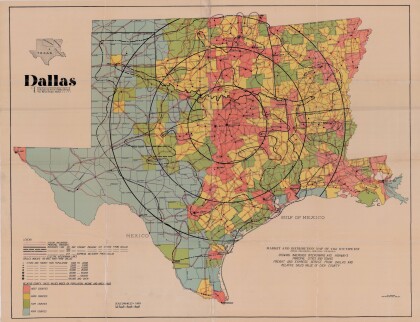
Dallas: Industrial and Distribution Center of the Southwest
Colorful market and distribution map of the Southwest - Texas, ...
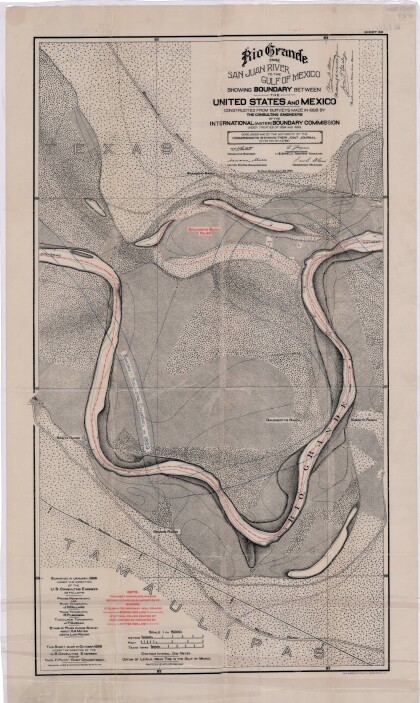
Rio Grande from San Juan River to the Gulf of Mexico
Map illustrates the Rio Grande from the San Juan River to the ...
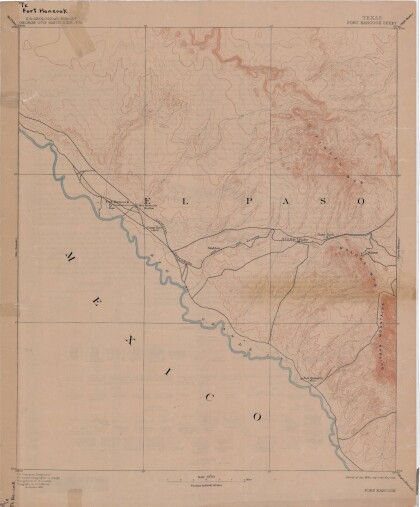
Map of Fort Hancock, Texas circa 1915
Topographical map indicating the location of Fort Hancock and ...
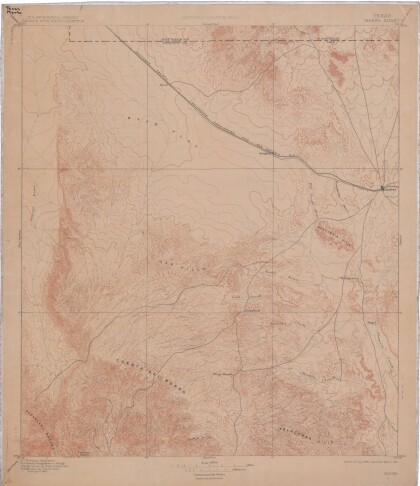
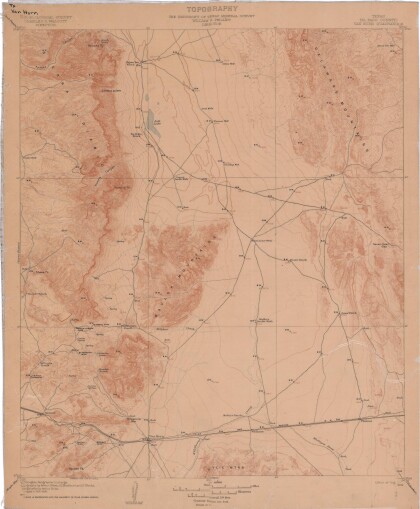
Topography: the University of Texas Mineral Survey
Topographic map of the Van Horn quadrangle in Texas. Indicates ...
J. De Cordova's State of Texas
This geographical map of Texas was compiled from the records of ...







Comments
Add a comment