Report this entry
More from the same community-collection
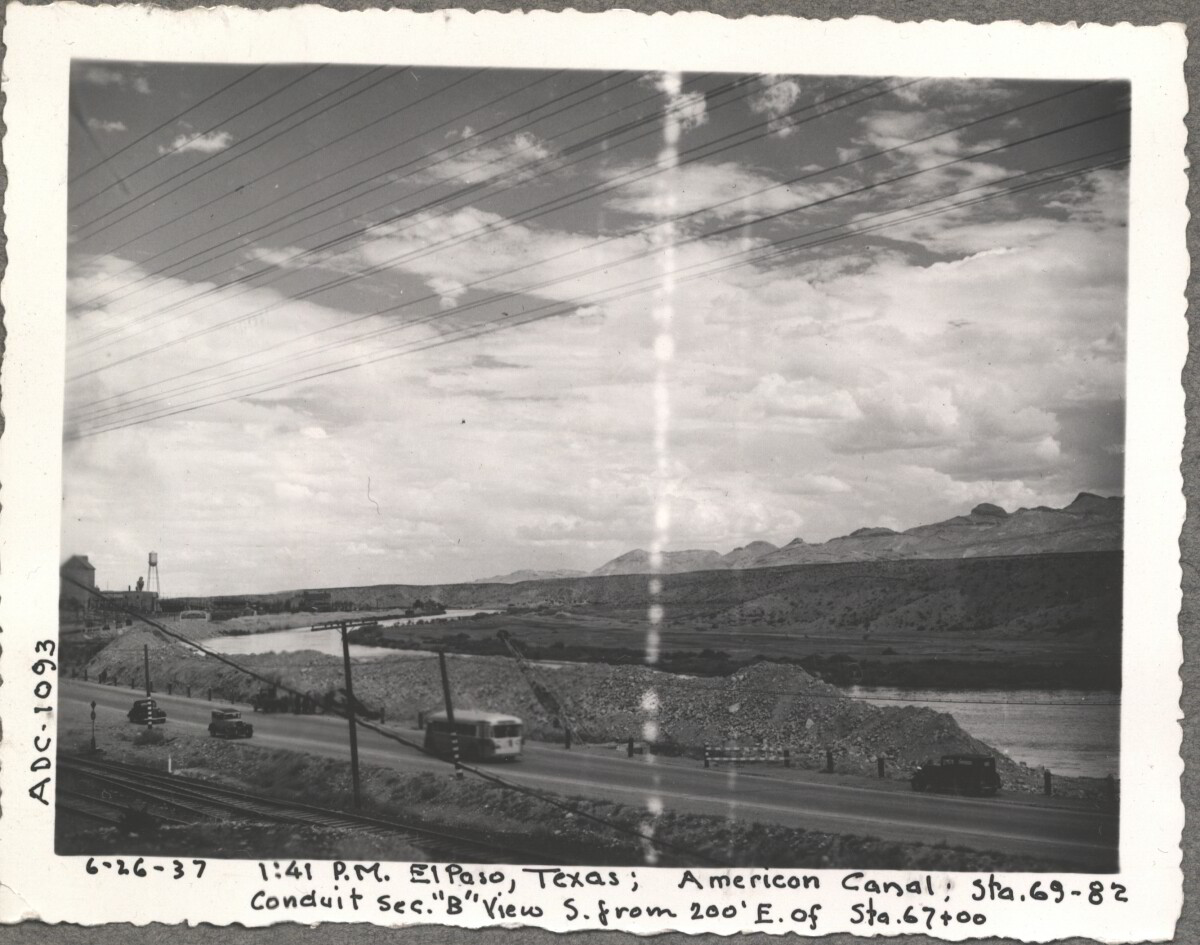
CELEBRATION OF THE 19TH AMENDMENT AT THE BURGES HOUSE.
Celebration of the centennial anniversary of the formal adoption ...
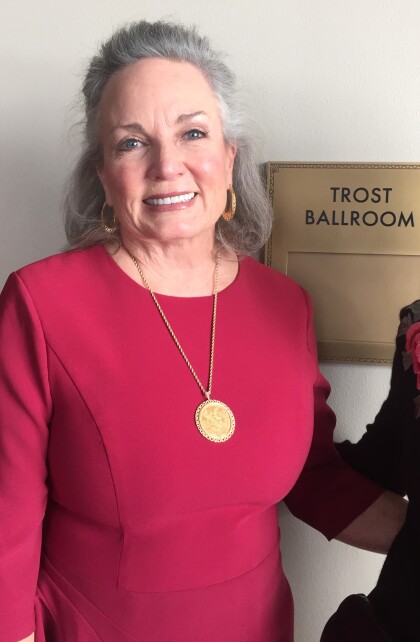
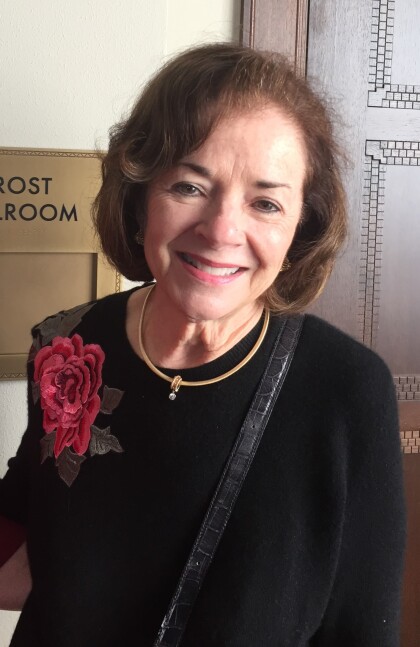
Women Attend Historical Society Hall of Honor FALL 2021
Attendees at the Historical Society Hall of Honor event on ...
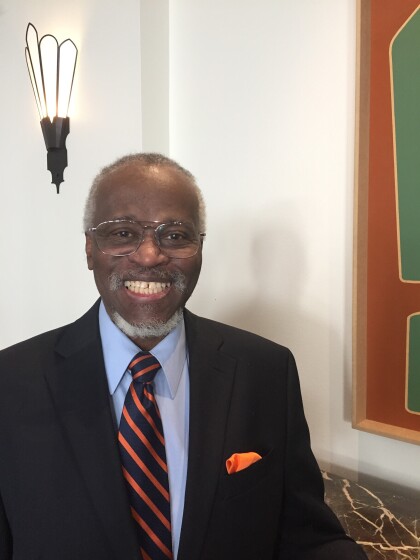
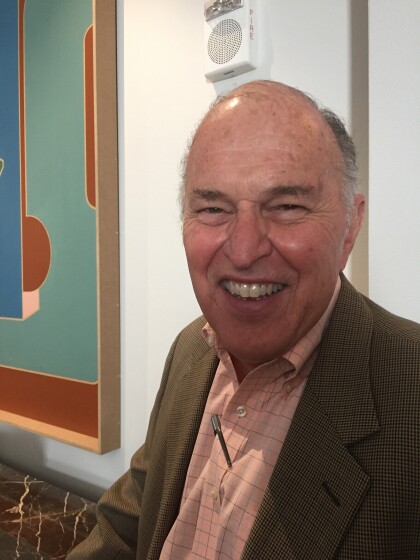
Donald Williams at the Historical Society HoF event
Donald Williams at the Historical Society Hall of Honor banquet ...
Janine Young, writer and historian
Janine Young, writer and historian El Paso County Historical ...
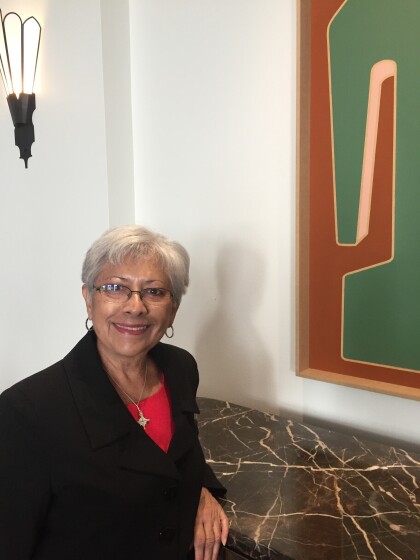
Ginger G. Francis at the Historical Society HoH
Ginger G. Francis graduated the Loretto Academy Class '75. She ...
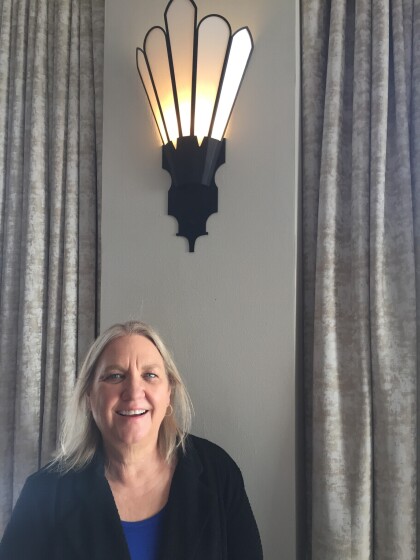
Hilda Stockmeyer Lewels, civic leader
Hilda Stockmeyer Lewels, civic leader at the November 14, 2021 ...
Downtown Main Library El Paso Texas November 2021
Downtown Main Library El Paso Texas under construction November ...
Gov Ann Richards quote and picture in downtown El Paos
Governor Ann Richards Honored in downtown El Paso, Texas by ...
WWII Photo from grandfather Fernandez Collection.
Photo belonging to my grandfather, Ramon Fernandez while he was ...







































Comments
Add a comment