Report this entry
More from the same community-collection
El Paso Police motorcycle officers - 1984
From the Left: Captain Tony Garganta, Severo Jimenez, Sgt. Dan ...
El Paso Police motorcycle officers - 1918
Capt. Joe Stowe and another officer inspecting new police ...
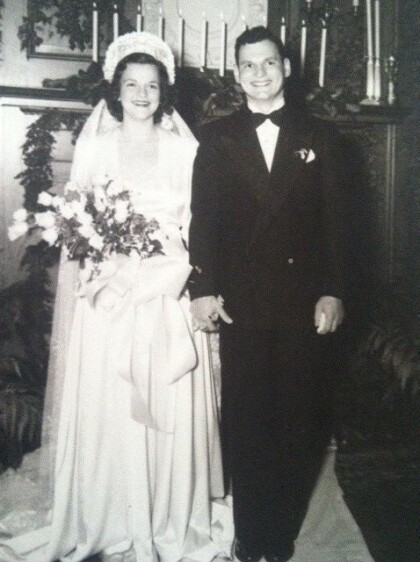
Ruth Schwartz Wedding Party - El Paso, Texas
Ruth Schwartz , daughter of Fannie & Adolph Schwartz ( Founder ...
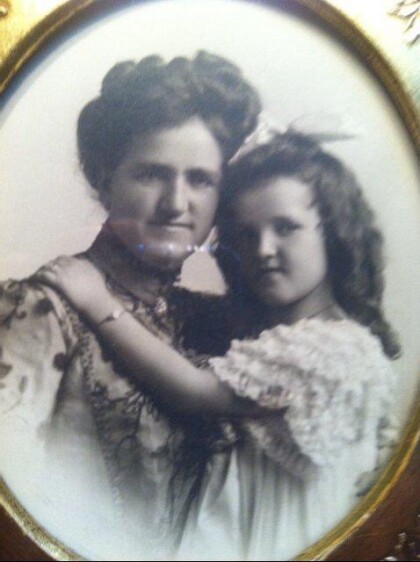
Ruth Schwartz Zork with Daughter Marian Eleanor Zork
Ruth Schwartz Zork , daughter of Adolph Schwartz with daughter ...
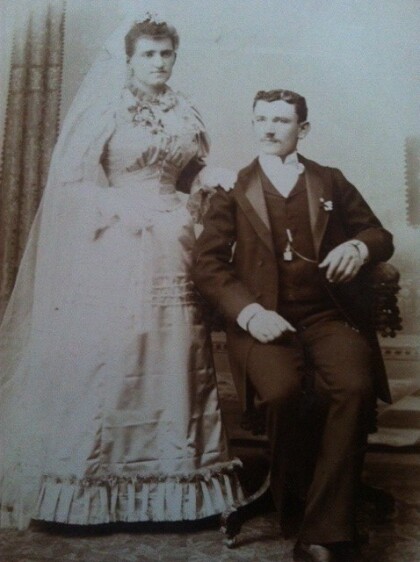
Adolph Schwartz founder of Popular Dry Good Co
Adolph Schwartz with his grandchildren Marian Eleanor Zork ( ...
El Paso Police Mounted Officers - 1974
left to right: Richards Edens, Karl Beasley, Al Kasten, Jim ...
El Paso Police Department - 1901 - El Paso, Texas
The El Paso City Police Department - 1901. A few short years ...
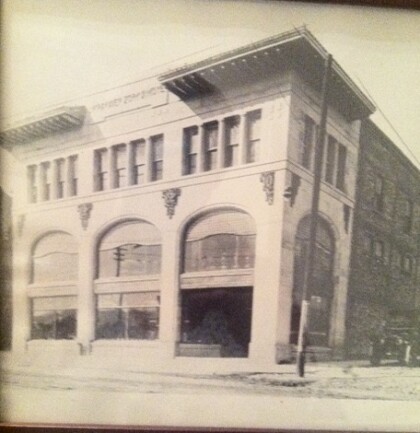
Krakauer,Zork and Moye, El Paso, Texas
Krakauer, Zork & Moye 117 San Francisco St. 1910( second ...
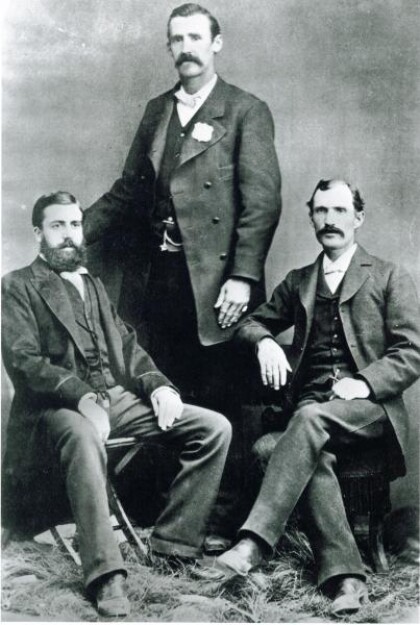
El Paso, Texas City Marshal Dallas Stoudenmire - 1881
El Paso City Marshall Dallas Stoudenmire with his deputy ...













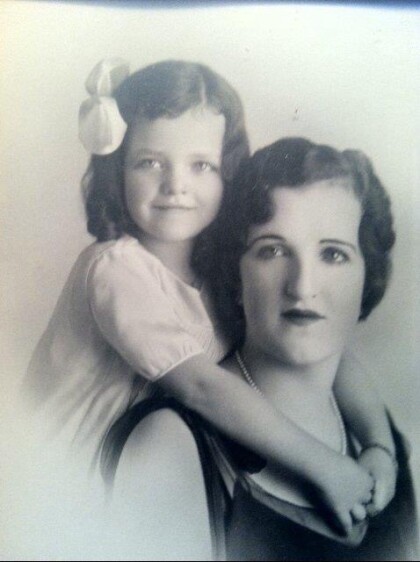

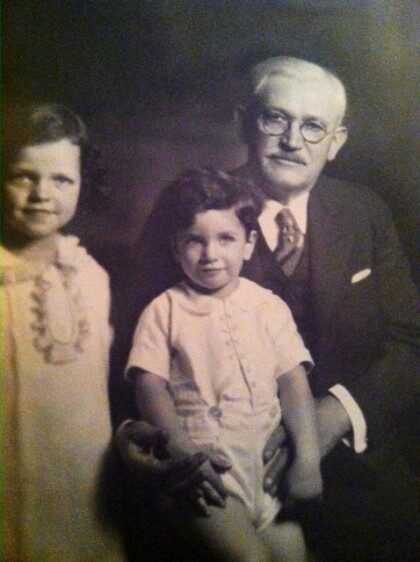














Comments
Add a comment